Overview
What is the supervysor?
Participating in a KYVE data pool such as Cosmoshub or Osmosis requires running two nodes: the KYVE protocol node and the data source node (e.g., full node of Cosmoshub, Osmosis, etc.). However, running these full nodes in parallel can result in high storage requirements (approximately 10TB for Osmosis), leading to increased operational costs and inefficient resource utilization. This inefficiency arises because the node begins synchronizing from the start, even though it only requires storage for a certain range of blocks. Additionally, the node lacks information about the progress of the KYVE pool and the already validated data, making pruning impractical when running a node as a KYVE data source.
However, if the synchronization process is halted, the node cannot fulfill its responsibilities as data source effectively. To overcome this challenge, the supervysor is introduced as a solution. The supervysor manages the data source node process based on the requirements of a KYVE data pool. It ensures that the node synchronizes only up to the necessary extent and continues to provide data even when the synchronization process is paused.
By implementing the supervysor, the synchronization process is optimized, reducing unnecessary storage usage and operational costs. The node can focus on synchronizing up to the required point, thus efficiently utilizing resources while fulfilling its role as a data source for the KYVE pool.
How does it work?
Structure
The supervysor is a process manager that is wrapped around a Tendermint node or the Cosmovisor. After the initial start, the node-height and the pool-height of the KYVE data pool are queried at a specified interval, after which the difference between the two values is calculated. If the difference is higher than height_difference_max, the node is set to the Ghost Mode. In this mode, the synchronization process is stopped by making the address book inaccessible and by starting the node without seeds and with a modified laddr. This ensures that the node cannot reach other peers and thus cannot synchronize new blocks. If the difference is smaller than height_difference_min, the address book is made accessible again and the node is started with specified seeds so that peers can be found and the synchronization process can continue. If the difference is smaller than height_difference_max and larger than height_difference_min the current mode is kept. In both modes, the endpoints are accessible to the protocol node, so the required data remains accessible even if the node does not synchronize.
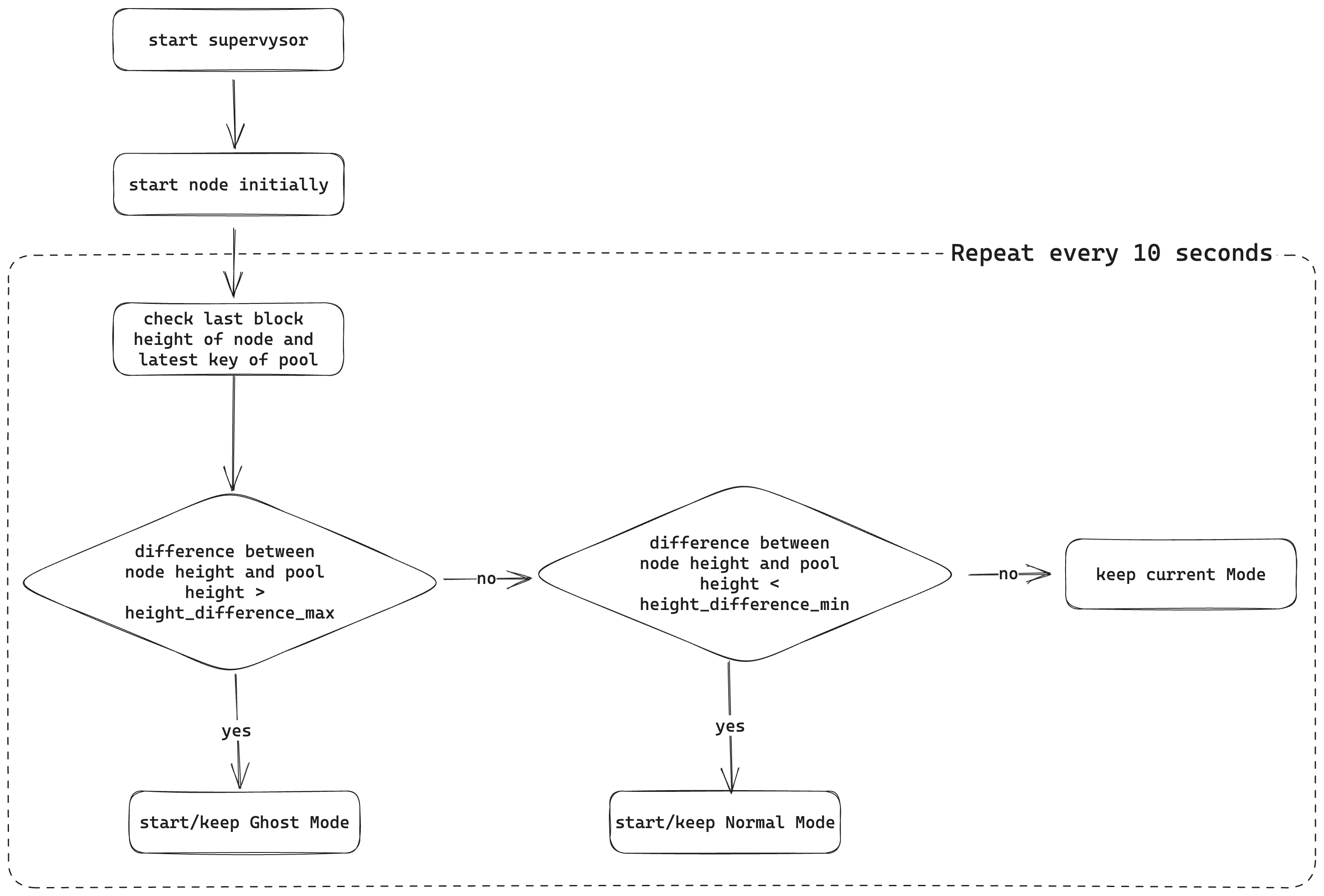
To keep memory requirements as low as possible, we need to specify both a maximum value for how far the data source node can synchronize beyond the current pool height and the matching pruning settings to make sure that data can only be pruned after validation. Derived from this, these values were calculated as followed:
height_difference_max = max_bundle_size / upload_interval * 60 * 60 * 24 * 2(maximum bundles for 2 days)- `height_difference_min = height_difference_max / 2 (maximum bundles for 1 day)
These values ensure that
- the data source node will always be 1 day ahead to the latest pool-height,
- the data source node will not sync to the latest height, because it will stop syncing when the required blocks for the next 2 days are stored locally,
- the data source node has a time window of 1 day to connect to peers to continue syncing before the pool catches up.
Pruning
Aside from the optimized syncing process, pruning already validated data is the second role of the supervysor to fulfill its goal of reducing disk storage requirements. Therefore, a custom pruning method is used, which relies on the provided Tendermint functionality of pruning all blocks until a specified height. In the context of the supervysor, this until-height should always be lower than the latest validated height of the KYVE data pool to ensure no data is pruned that needs validation. Unfortunately, the node has to be stopped to execute the pruning process, while a pruning-interval needs specification in hours. During this interval, the supervysor halts the current node process, prunes all validated blocks, and restarts the node. Due to the required time to connect with peers and to prevent the pool from catching up with the node, the pruning process is only initiated if the node is in GhostMode. If the node is in NormalMode, even if the interval reaches the pruning threshold, pruning will be enabled immediately after the node enters GhostMode. Additionally, it is recommended to set the pruning-interval to a value of at least six hours to ensure there is enough time to find peers before the pool catches up.