Postgres Destination
This page will guide you through setting up an ELT pipeline to fetch data from
a KYVE data pool and import it into a local Postgres database.
Postgres Setup
In this step, you will deploy a local Postgres database using Docker.
Run the following command to create a container with the latest Postgres image:
docker run --name local-psql -v local_psql_data:/var/lib/postgresql/data -p 5432:5432 -e POSTGRES_PASSWORD=pass -d postgresAccess the Postgres terminal to set up a database for the pipeline's destination:
docker exec -it local-psql psql -U postgresIn the Postgres terminal, run the following commands:
CREATE DATABASE kyvetest;CREATE USER airbyte_user WITH ENCRYPTED PASSWORD 'pass';GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON DATABASE kyvetest to airbyte_user;\connect kyvetestGRANT ALL ON SCHEMA public to airbyte_user;\quitA database named
kyvetesthas been created and the userairbyte_userwith passwordpassnow has read and write access.Install the pgAdmin 4 Postgres management tool, for example with Homebrew:
brew install --cask pgadmin4Run pgAdmin and click on "Add New Server". Give it a name, for example
local-psql, and in the "Connections" tab fill out the fields as follows:- Host name/address:
localhost - Maintenance database:
kyvetest - Username:
airbyte_user - Password:
pass(in case you did not modify it in step 3)
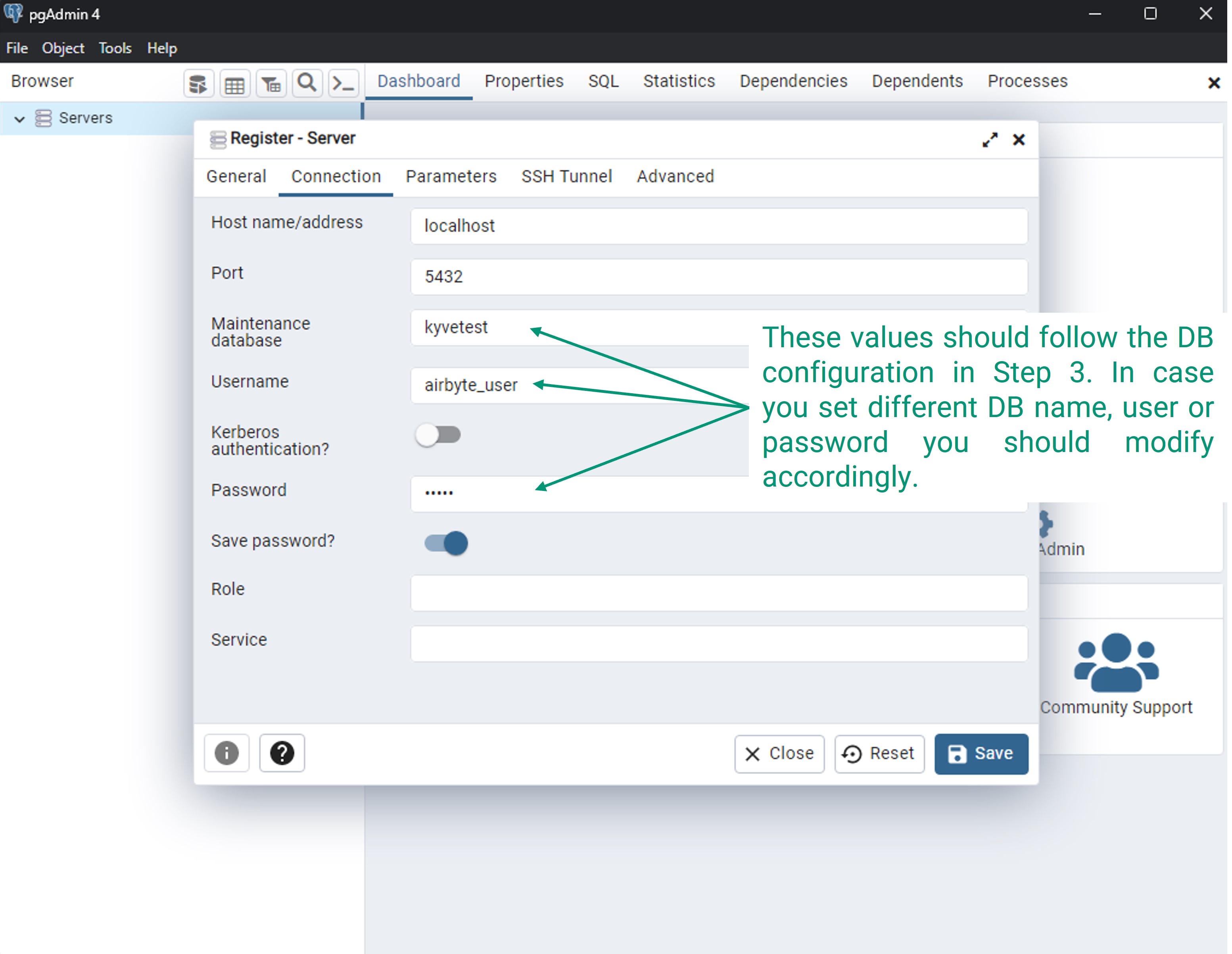
- Host name/address:
Configure Airbyte
This example uses old data from the devnet. Check out
https://app.kyve.network/#/pools
to get a list of active mainnet pools.
Here, we can recommend Osmosis (pool_id: 1) or Archway (pool_id: 2)
Now you're ready to create the connection in Airbyte (http://localhost:8000/).
Set up the source.
Search for "KYVE" in the
Sourcessearch bar and select it.In this step you specify the KYVE pools from which you want to retrieve data, identified by Pool-IDs.
You can also specify Bundle-Start-IDs for each pool, in order to limit the records that will be retrieved from that pool. In the KYVE app you can find the bundles for each pool, for example these are the bundles for Pool-ID
8, the Evmos chain.For this example we choose to ingest only the Evmos chain.
- Source Name: KYVE
- Pool-IDs:
8 - Bundle-Start-IDs:
105395 - KYVE-API URL Base: The base URL indicates the KYVE network
Mainnet: https://api-eu-1.kyve.networkTestnet: https://api-eu-1.kaon.kyve.network/Devnet: https://api.korellia.kyve.network/
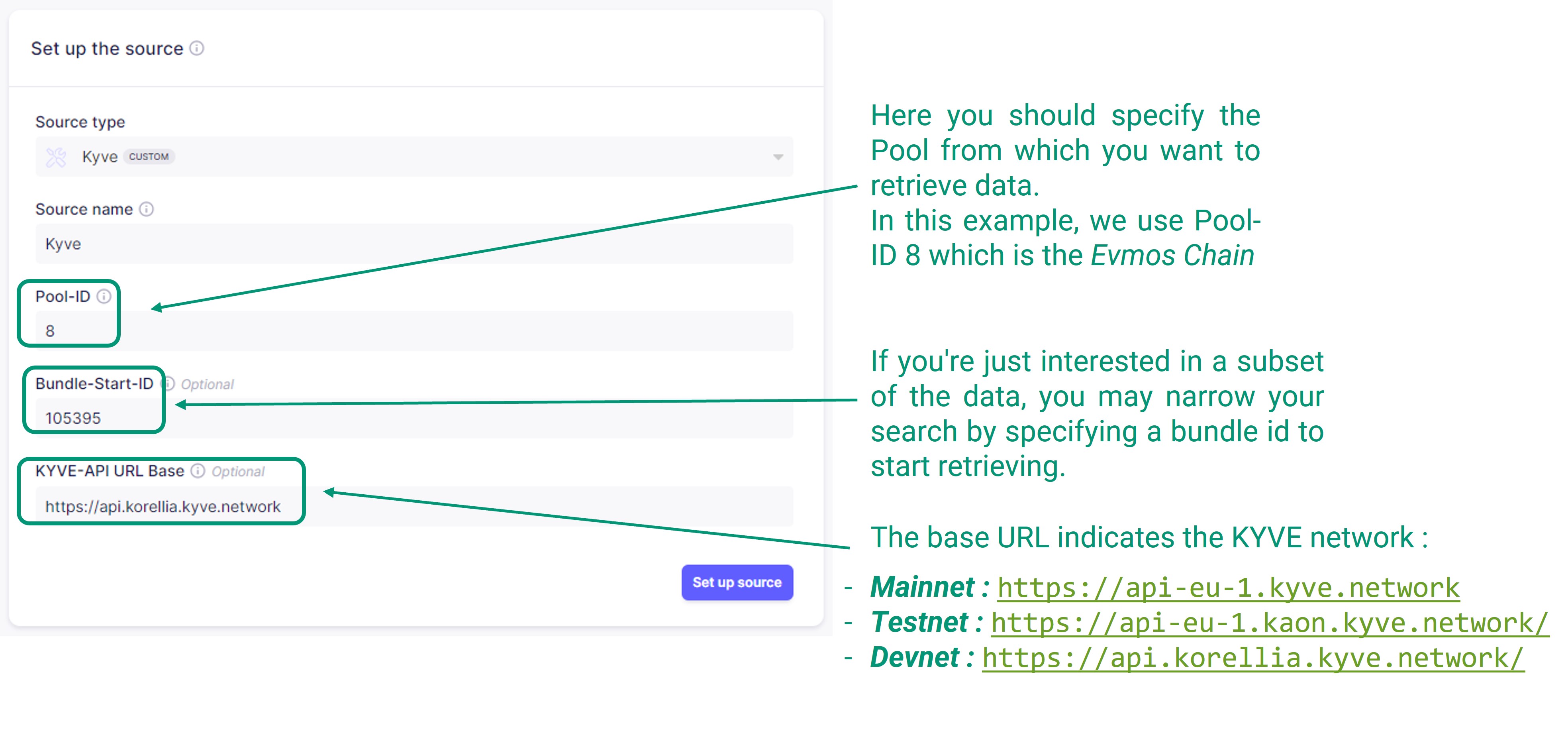
NOTE: The Bundle-Start-IDs determines the size of the extracted data. This also affects the time required for completing the sync process, up to several hours for historic data. It is advised for testing purposes to visit the KYVE network Polls page and to select a recent bundle ID (2-5 days old).
Set up the destination.
Search for "Postgres" in the
Destinationssearch bar and select it.Add the parameters of the Postgres DB that you configured here:
- Destination type: Postgres Local
- DB Name:
kyvetest - User:
airbyte_user - Password:
pass
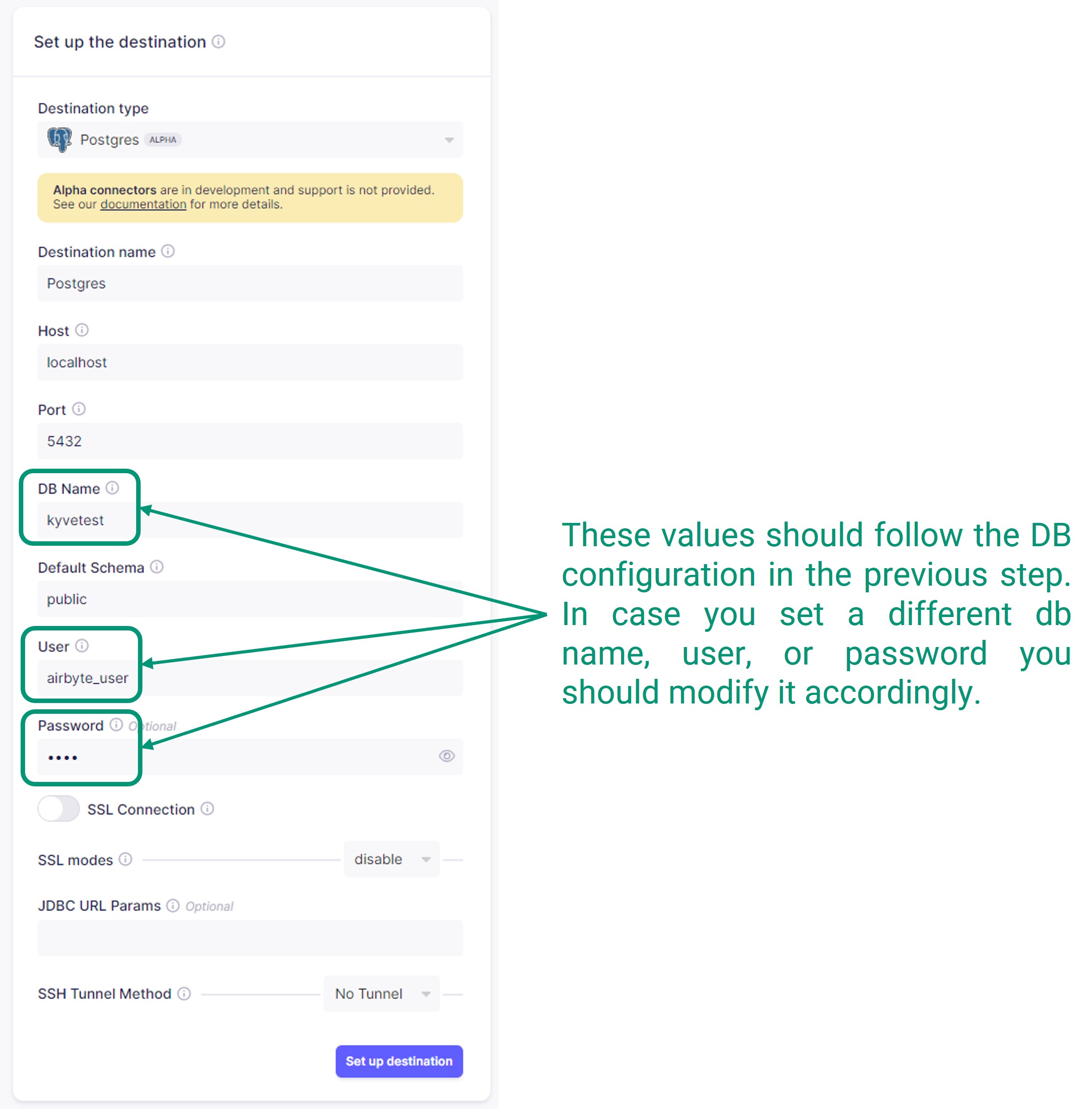
Final ELT configuration.
Select the
KYVE Sourcethat you have configured in step 1 and thePostgres Destinationfrom step 2. In this step you can make final modifications to the pipeline.- In the Transfer field, you can set how often the data should sync to the destination. For this example, we set it to
Manual. - In the Streams section, you can modify the Namespace, and you can add a Prefix for the data that will be stored. In this example we added the word
evmosso the tables in postgres will be namedevmospool_0_.... - In the Activate the streams you want to sync section, you can modify the behavior of the stream in each repetition. For this example, you could set it to
Incremental|Append, which means that only new records will be stored on each new sync and will be appended in the DB.
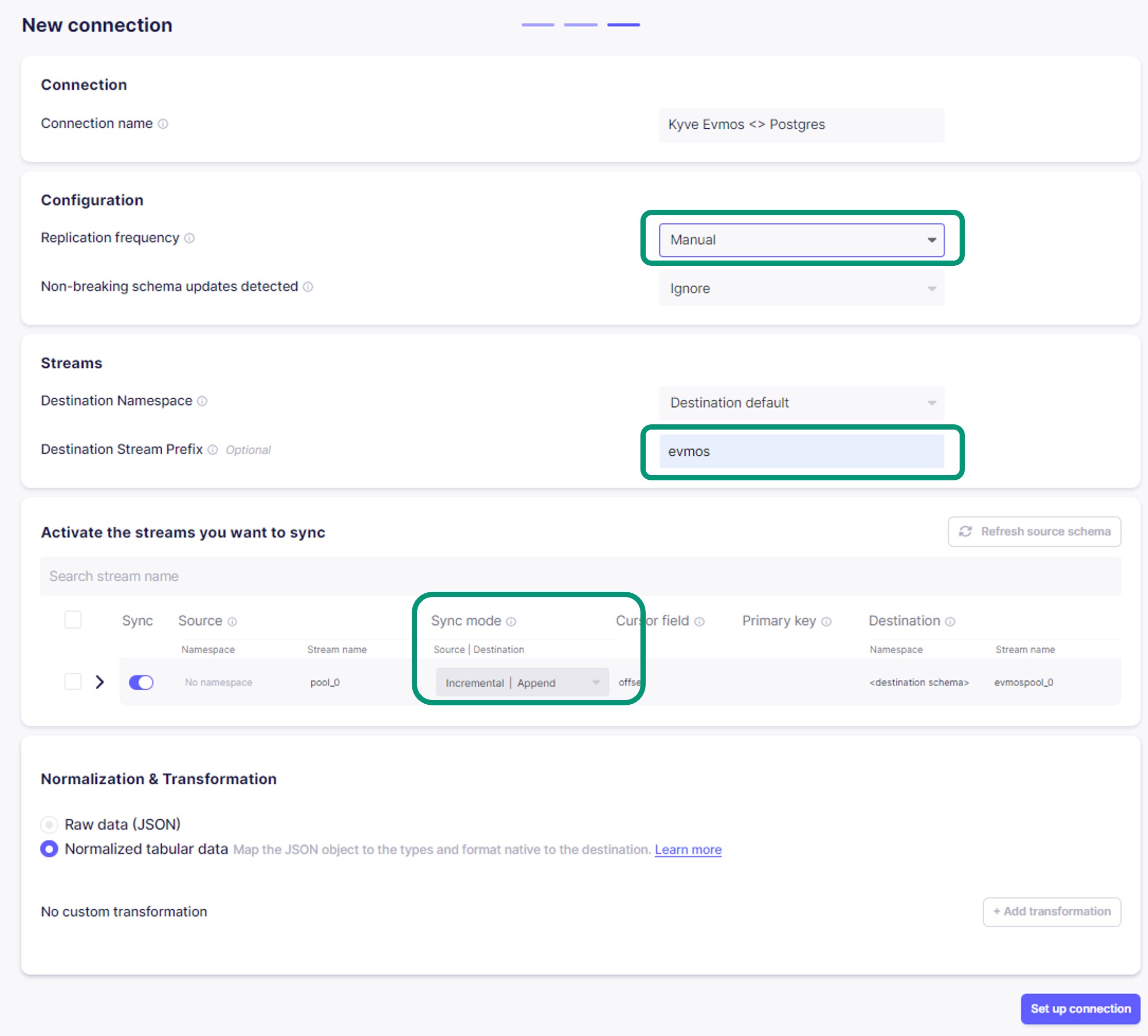
- In the Transfer field, you can set how often the data should sync to the destination. For this example, we set it to
Run the initial sync.
Click Sync Now. You can track progress by clicking "Sync Running". Depending on how you configured the source in Step 1 this may take a while.
View Stored Data
For viewing the retrieved data, open pgAdmin (or any other Postgres management tool that you have installed) and connect to the kyvetest database that you created in Step 3.
In the public schema, you will find the retrieved records in both raw and normalized formats.
Raw format
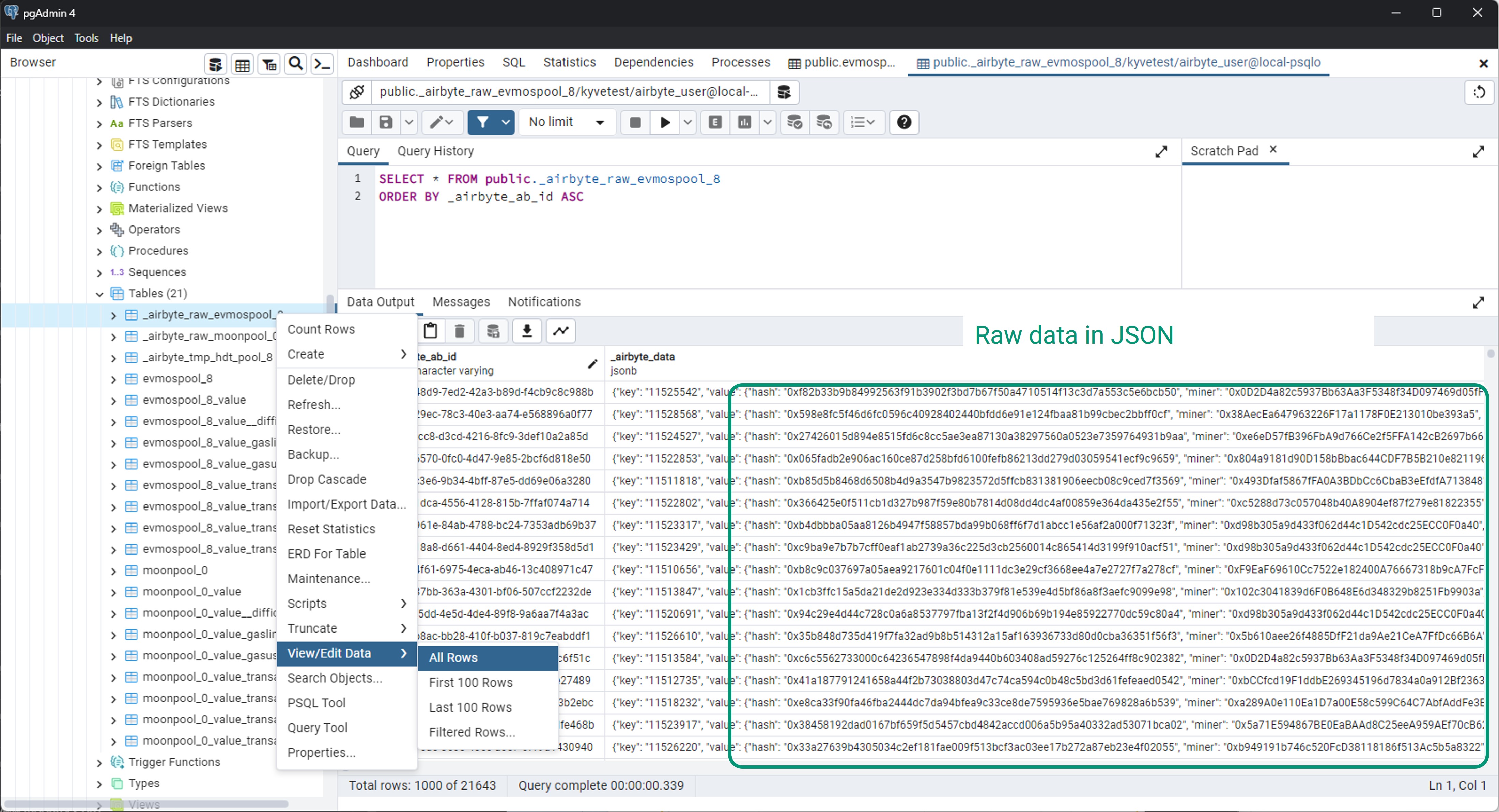
Normalized format
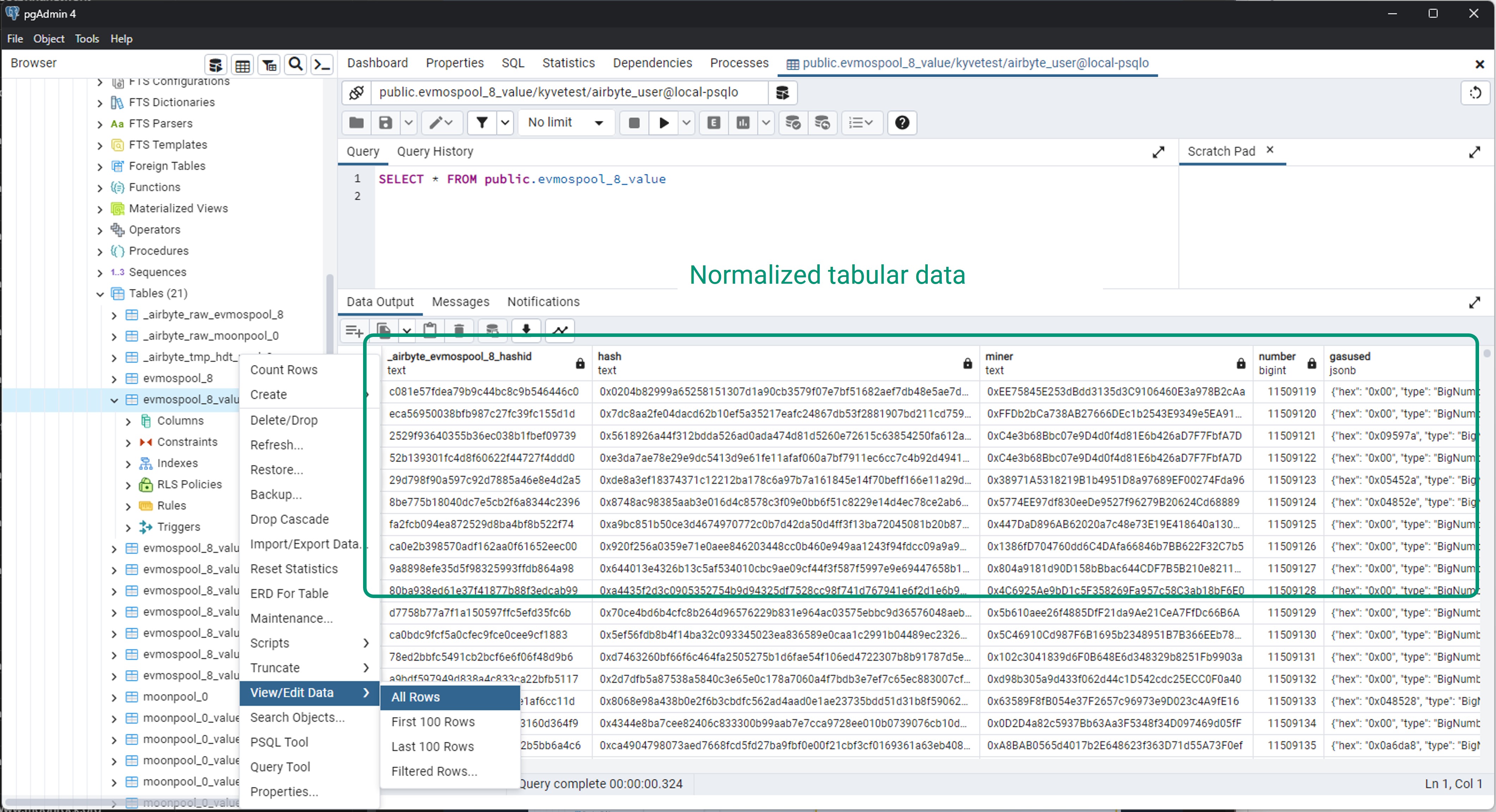
That's it! You've successfully created an end-to-end ELT pipeline fetching data from a KYVE data pool and importing it into a local Postgres database.